Principle A systems approach to management
Synthesis of the Problem before Analysis
Understanding the System with sub-systems or the collection of all parts in a whole to better understand with various parts connecting together for a greater purpose.
Corporate Strategy - Execution of the Strategy to enable Business Strategy
Architecture must align the many parts of the organization to meet the corporate strategy. The execution of the operational strategy is considered a performance measure and external stakeholders require the organization to be audited by an external audit company.
Maturity of an organization or agency
If we measure an organization or agency for their maturity, we look to understand the effectiveness of the organization or agencies ability to meet the estimated or investment plans.
The strategy looks at the various parts as they relate to the whole enterprise.
The people, offers and how we segment the cost and benefits first must segment the workers, suppliers and customers based on known and knowable situations.
Party Management Capability a people system
In a people centered design strategy we focus on the interactions between people.
Competency Tiers
An employer to the workers and competencies each role must have within the business function according to the complexity of work we need the person to perform.
a) Basic or Entry level up to a 1st level certification
b) Advanced level acquires a 1st level certification and a 2nd level advanced certification
c) Expert level acquires both 1st and 2nd level certifications and recognition amongst industry professionals.
Each tier represent a place to measure leverage points throughput and effectiveness of your execution of the strategy.
The feedback loops enable continuous improvement of your leadership based on employee performance and workers sentiment.
Measuring Capabilities as sub-systems within a system - Re-use as a leverage point
We execute the business strategy and want to understand the "throughput" in three different levels of complexity. The volume and speed changes as we observe and understand design patterns in relationship with complexity or maturity of an offer.
Level 2 in the Business Process Hierarchy
The common points in a process is shown below in the diagram from Process 1 to all other Processes at level 2.
Level 2 to Level 3 in Business Process Hierarchy
A business process incorporates a series of activities, organized as task in a pre-defined process by using feedback loops at each point between two swim lanes.
 |
| 1. Design Strategy and Vision with Expense Transaction Capability |
Private Sector
Applies to all business leaders with people or budget management responsibility
Enables an organization to measure the performance of cost against the plan (investment to execute strategy)
Public Sector
Applies to all leaders within any branch of government or any agency, assume the process in which an estimate is supplied to an accountable agency (typically the Treasury).
An estimated cost and benefit request is reviewed by the treasury agency and may include a service to assist the branch resources with preparing to submit a request to the cabinet or congress.
Measuring Leadership Competencies
A feedback loop enables leadership measures based on the ability for leaders to the meet the estimated cost according to the plan.
Others may refer to this feedback loop a measurement used to evaluate your management competencies. An organizations value is measured by the competencies of their leadership capabilities.
In business language the opportunity we introduce using systems enables the organization or agency to effectively and consistently measure management competencies by the leaders ability to forecast and execute the strategy.
Offer Management Capability a service management strategy
Estimating the cost of a portfolio
A portfolio would best describe a business group in the private sector.
A portfolio would best describe a branch of the government in public sector.
A portfolio consist of different programs or consider a program a part of a whole.
One approach which aligns well to international and emerging standards from an Enterprise Architecture and Enterprise as a System we can see sub-system patterns amongst the systems.
Programs may have a series of projects executed in parallel to each other or others in a program which is a sub-part of a portfolio.
- Basic or general complexity
- Advanced complexity
- Serious complexity
The names used by each complexity tier, isn't going to align well. The behaviors we can expect help us to align our expectations and plan based on known or knowable situations.
Estimation of cost for a project
A project has a begin date and planned end date.
Effectiveness of the project team to meet the goals of the project within budget and on-time often will be better if your project team has more experience. Human dynamics and the ability for the team to interact well together is going to play a part in the projects success.
Exepense Transaction Capabilities for IT and Business
An expense transaction capability ensures the Financial Management process for IT, while enabling the same concept for business users. A universally significant business service.
Every branch of the government will estimate cost to supply services through a branch who either contracts to a service provider or serves the citizens directly.
As the corporate strategy is revisited each year we conclude the efforts with an implementation. A post planning task performed to enable business strategy.
The quality management system is the most common name associated with the audit report and findings. Many people are unaware that investors and shareholders use the audit report as a way to measure the effectiveness of the Executives.
Business Strategy - Execution of the Strategy to enable Operational Strategy
A Task Level View
Entry of the agreed Budget allocations or Estimated Portfolio/Project cost.
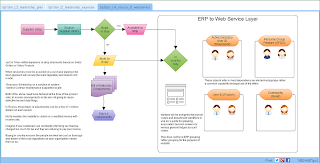
The task output must include an event record.
An outcome of the capability
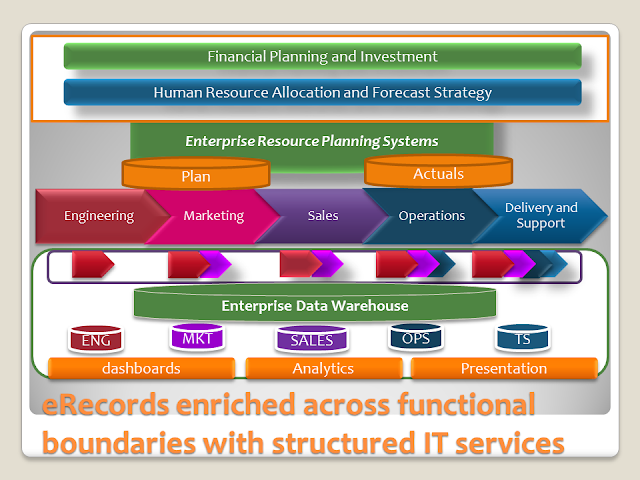
The following diagram indicates the architecture and sub-system views for storage and record retention for recovery time objectives for the financial management component within a service management strategy.

Private Sector - General Cost Accounting
An ERP journal entry represents the activity or event record during execution of the operational task.
Public Sector - Estimation of Cost
An ERP journal entry represents the activity or event record during execution of the operational task.
Output - Corporate Strategy transitions to Business Strategy Implementation
A decision from swimlane 1 Design Strategy and Vision at Level 2 to swimlane(s) 2-5
During the design strategy and vision we experience the request from various business function leaders. Typically, the Profit and Loss owner begins with the prior years investment amounts allocated within their functional hierarchy.
a) Resource cost - current resource expense, fully loaded cost associated with a full time workers. Fully loaded for a consultant or contractor. Fully loaded temporary workers.
b) Resource cost - Planned future hires by quarter, known consulting recurring cost to initiate a new product or service and strategy.
will adjust a positive value into a general ledger code then segment by department account code, with a company code.
Segmentation of
financials must use natural hierarchies. Strong hierarchies are another way to describe well defined data structured to organize in a consistent manner.
The chart of accounts and sales journal typically ensure the following segmentation systematically as canned reports from your ERP system.
- Company Code
- Location Code
- General Ledger Account Code
- Sub-Account Code
- Project Code
- Department Code
Ideally, the user defaults the values with an override
variables within the range of the user span of control.
If a user supports more than one department, the range of the departments must be approved up to the P&L owner. A standard operating procedure may be introduced to default this authority when defined and authorized as a business policy.
Principle A process approach
1. Design Strategy and Vision
Executives working closely with Human Resources and Corporate Finance manage the business leaders inputs to the annual planning process.
Inclusive of this process would be the investments in people and plan to acquire new people with new or existing skills.
Services offered to all functional organizations and leaders across an organization are authorized by the Design Strategy and Vision process. An annual process enabling all private sector business functions and all public sector branches or agencies.
Private Sector -
2. Develop Products and Services
Product development plans with associated budgets by types of offers. Another way to manage the complexity would be to isolate and protect your innovation and advanced offers into three different business models.
People skills and wisdom are vital to the success of an innovation product versus the core or advanced skills. Ideally, advanced has a higher skill than Core.
Each has various degrees of complexity especially when your organizational design has not segregated the different business needs.
Example; each product development life cycle has a process known as Research and Development. The Core offers are light in R&D, Advanced has greater R&D and Innovation may be primarily R&D.
3. Market and Sell Products and Services

The market and sell products and services process is downstream to the Develop Products and Services
4. Deliver Products and Services
5. Manage Products and Services