Party ManagementA party management capability intends to prescribe the effective manner in which to present a business service from management capability to transaction capability.
Travelers
Continuing our highway analogy we intend to drill into the drivers and the vehicles make, model and colors as we build our performance measures the different types of combinations to guide decision making.
Types of activities in either scenario
- Party, Offer, and Financial Account Management Capabilities
- Expense and Revenue Transaction Capabilities
Management Capabilities
Three of the five capabilities contain the user group with accountability and authority to set up a new, update an existing and archive any of the master records. NEVER DELETE
All three of the management capabilities have countless records in each category.
Create, Read, Update and Archive master records
The users are typically experienced and well versed in corporate policies, inclusive of the legal points within the process which they run their daily activities.
The system of record MUST be the organization or agencies ERP or accounting system.
Transaction Capabilities
- Expense Transaction Capabilities
- Revenue Transaction Capabilities
Each of these two capabilities requires the ability to source master records from the system of record. The transaction capability allows the user to create a transaction with reference data from the system of record.
Each of the three will be referenced on transactions and validate performed during the accounting close procedures to mature the transaction to a RECORD.
The first data set which must be controlled begins with "user" types or access and entitlement for any new transaction, does the user have the knowledge to "sell" the offer and does the user have the authority to sell to the customer selected. A user should only be allowed to select a customer master record if they are assigned to the customer.
Security and Zero Data Loss (ZDL)
Customer master records are confidential and expectations are high that an organization or agency protects the customer master record and all transactions are maintained for at least seven years (ZDL)
Business Services
We can assume on each of the transaction capability outcomes are best designed as business services.
We can assume a collection of business process task and activities will be children to the transaction capabilities.
We can assume that no transaction would presume a change to the master record. In fact, the opposite being only retention of the record and an update pending customer approval.
ERP systems have the features designed within the application and these systems have been designed to perform accounting activities systematically.
When ERP master records are updated frequently we see many adjustments or longer close periods.
True or False
A. During a users processing a transaction, the user must have the authority to CREATE a new customer management record. On demand customer create capability
FALSE
- An update to a master record, must be authorized by the customer in writing, the mutual evidence of arrangement details the expectations in this scenario.
- In the case of small and medium businesses the process may allow for a request to create a customer master record, PUSH the request to the authorized representatives in the master record workflow.
- Any new master record must perform "due diligence" in any new customer management record or be excluded from revenue.
B. During transaction processing a change to a segment of the master record must be executed on demand.
FALSE
-
No, the legal terms and conditions must be met which requires a formal change management process. A customers authorized representative MUST sign a change record request.
- Your master record workflow roles must perform due diligence before a transaction can be recorded as revenue.
1. A transaction event READs and captures the POINT IN TIME reference data.
There are Sarbanes Oxley Act of 2002 Key Controls(more than five per transaction) which must be logged and documented.
An organization must design effective key controls
An organization must segregate duties between the users who create, authorize who reads, updates and archives any master record.
An organization must segregate duties between the users who create a transaction
The segregation of duties must also segregate the business users and IT users in both categories.
No person or user should have access to create a management record of any type and must not have an ability to create a transaction.
which must record any change to any master record which must have documented due diligence performed before a master record is created.
2. An update to a master record during transaction processing fails to meet the due diligence rule and would not be a situation which would be brought forward by the transaction user group.
Segregation of Duties
A key control under Sarbanes-Oxley Act infers that revenue must be excluded when due diligence fails or a supplier fails to perform due diligence.

Effective Key Controls are proven in external audit activities under financial audit and re-certification to international standards would be highlighted by the external auditor.
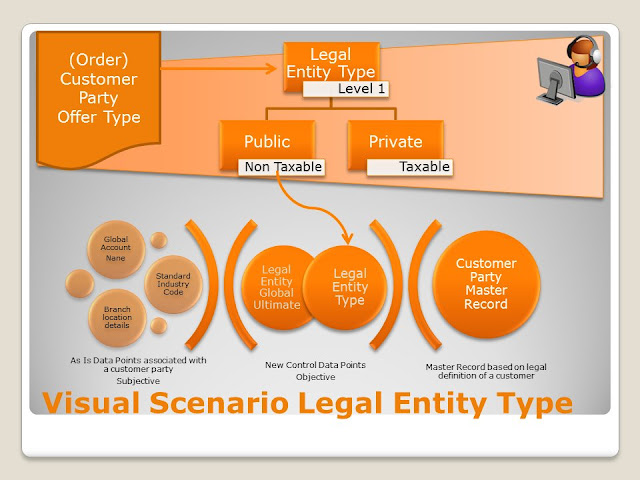
We have the management focus which relates to the create, read, update and archive capability for the PARTY roles internally and externally.
Drivers
These are the level 2 values in any party management capability. What's important about these variables.
- Person Party
- Employee Worker-Organization Party
- Contract Worker-Supplier Party
- Temporary Worker-Supplier Party
- Download User - Customer Party
- One record for every consumer
Motor Vehicle Buy and Mfg.
Motor vehicle traveling in either direction
- Organization Party
- Customer Party
- North Bound entry onto highway - revenue transaction capability
- Supplier Party
- South Bound entry onto highway - expense transaction capability